Purpose
The purpose of this operations manual is to outline ETISE operations including how to perform a smart manufacturing for energy management assessment, and other operations including organizational hierarchy, equipment, safety, website, training materials, and regional manufacturer database.
Introduction
The East Tennessee Initiative for Smart Energy Management (ETISE) was founded by the University of Tennessee, Knoxville along with the UT Center for Industrial Services (CIS) and Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) to promote integration of smart manufacturing (SM) for energy management in the nation through innovative technical assistance and workforce training.
Using East Tennessee as a test bed, ETISE will pursue these three objectives:
- Understand how to implement SM for energy management by industries and sizes in the region,
- Develop a technical assistance and workforce training model at the regional level through ground service to manufacturers in East Tennessee, and
- Make strategic suggestions to DOE and AMO that will promote the adoption of SM for energy management.
ETISE Organization Structure
Figure 1 shows the organizational structure of the ETISE team and each team member’s major role, but many tasks will be a collaboration among multiple team members.
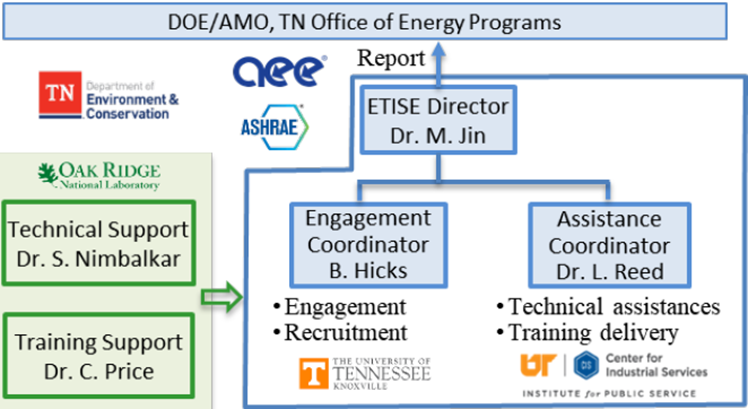
Figure 1: ETISE organization structure
Project Management Plan
ETISE will use Teamwork Project for project management, including Gantt Charts, reporting, messaging, time tracking, and file sharing through Microsoft Teams at UT. A master Gantt chart will be followed throughout the project. The team will share files and data through Teamwork Project, connected to Microsoft Teams, which all teams have used during proposal development. There will be individual reports for all activities, plus quarterly progress reports and annual reports.
Equipment Guidelines
Suggested equipment for performing a smart energy management assessment include:
- Safety equipment including hard hat, ear plugs, high visibility vests, and safety glasses
- Tape measure
- Multimeter / Voltmeter / Ammeter / Wattmeter
- Lighting meter / lux meter
- Anemometer (wind speed)
- Infrared thermometer gun
- Probe thermometer
- Flue gas sensor / combustion analyzer
- Data loggers
- Fluke power logger
- Computer with fluke and other softwares installed
Optional equipment:
- Digital pressure gauge
- CO2 meter
- Smoke generator
- Flow meter
- Glass thickness gauge
- Manometer gauge – low pressure
- Pitot tube – fluid velocity
- Dewpoint hygrometer – moisture content
- Psychrometer – air humidity
Equipment should be stored safely in suitcases provided while it is not being used.
Checklists should be used for keeping a record of the equipment in suitcases.
Make sure that equipment is charged, and extra batteries are packed before each audit.
The student should provide notebook and pen, appropriate clothing for the plant floor, and a phone or camera, flashlight, and calculator.
Safety Guidelines
Before starting any tour, the entire audit team should be thoroughly briefed on equipment and plant procedures.
Adequate safety equipment should be worn on the plant floor including but not limited to steel toed boots, ear plugs, safety glasses, hard, and high visibility vest.
Notify an operator before approaching equipment. Practice caution while examining operating equipment.
Rely on plant electricians for electrical measurements.
Stay within designated walking paths.
Website
The website is located at https://etise.utk.edu/. The website should be kept up to date with any news articles, social media posts, or updates from ETISE.
Performing a Smart Energy Management Assessment
Step 1: Pre-Assessment Information Gathering
- Size of plant and plant layout
- Industry type (SIC / NAICS code) and process description
- Production levels, units and dollars, operating hours
- One year history of utility bills
- List of major energy consuming equipment
- ETISE survey on smart manufacturing
Step 2: Ensure that key plant personnel are involved
- Plant Manager
- Energy Manager
- Environmental personnel
- Maintenance personnel
- IT
Step 3: Pre-Assessment Analysis
- Analyze the manufacturing process
- Chart and graph utility bills
- Analyze utility bills for trends and errors; establish unit cost of energy
- Create plant profile using Plant Energy Profiler Tool – Plant Energy Profiler Excel
- Identify key energy systems
- Review design and other technical documentations
- Identify potential smart manufacturing for energy management recommendations
- Develop assessment day strategy
Step 4: Day of Assessment
- Introduction
- Roundtable introductions, intro to ETISE program
- Distribute BP tools, case studies, tip sheets
- Description of manufacturing process and operations
- Is this a typical day?
- Run through process following material flow
- Discussion of existing IT architecture and energy management process
- Questions about defects, bottle necks, data silos, interconnection
- Present charts and tables of utility bills
- Plant Tour
- Conduct in the direction of material flow
- Maintenance or floor leader to conduct tour with support from plant manager
- Conceptual tour, identify areas for smart manufacturing improvements
- Meeting room debriefing
- Discuss process, ask questions
- Develop plan for afternoon and create specific tasks
- Review notes and brainstorm (Working Lunch)
- Develop list of potential smart manufacturing and energy management opportunities
- Ensure that everyone has clarity of process and potential recommendations
- Refine list of opportunities to be investigated
- Decide what information needs to be gathered, measured, monitored
- Assign specific tasks
- Make plan to finish at assigned time and place
- Data Gathering
- Conduct measurements, monitoring, and diagnostic testing
- Energy management process
- Decarbonization
- ITData practices
- Building systems
- Conduct measurements, monitoring, and diagnostic testing
- Exit Interview
- Discuss findings with management
- Preliminary estimate of potential recommendations
- Prioritize recommendations
Step 5: Post Assessment Activities
- Conduct engineering and financial analysis
- Develop first order estimates of implementation cost
- Deliver report to client
- Contents of Report
- Executive summary including summary of recommendations
- Plant descriptionProcess description
- Resource charts and tables
- Major energy consuming equipment
- Best practices
- Smart manufacturing recommendations
- Energy management recommendations
- Follow-up to Report
- Call client two week to ensure report delivery and answer questions
- Call client in 6-9 months for implementation data
